The Best Fluffy Pancakes recipe you will fall in love with. Full of tips and tricks to help you make the best pancakes.
Beginner’s Guide to Mountain Biking
Gear, technique, and trail etiquette for those new to MTB.
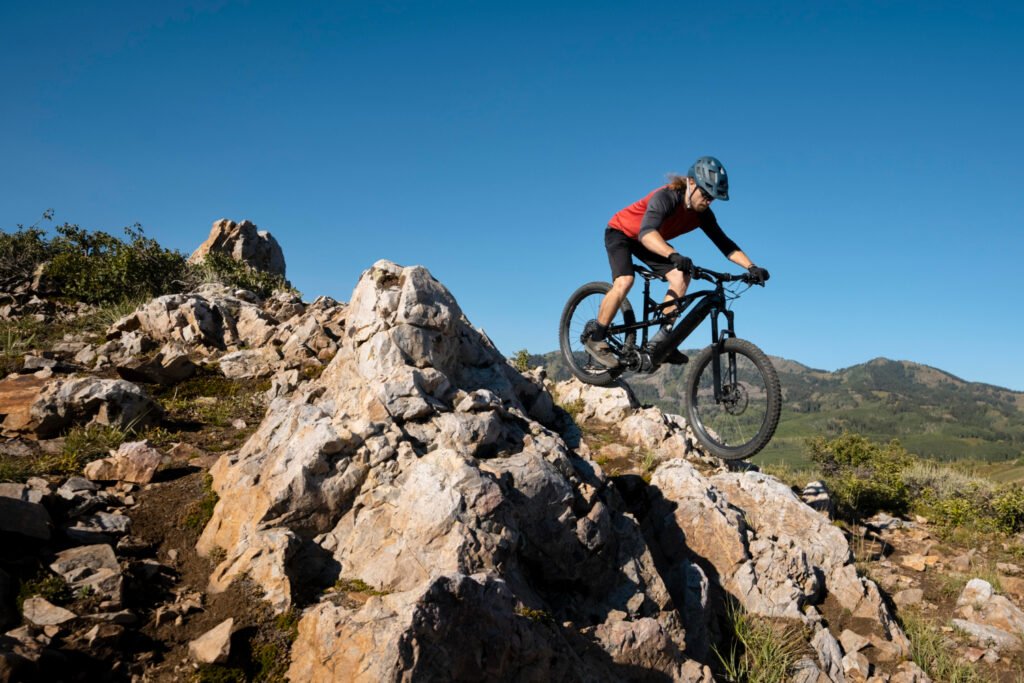

Mountain biking opens up an exciting world of adventure, fitness, and exploration. For beginners, however, the sport can feel intimidating—steep trails, technical features, and unfamiliar gear all create a steep learning curve. With the right approach, you can ease into mountain biking safely while building confidence and skills that last a lifetime.
This guide covers essential beginner gear, fundamental techniques, trail etiquette, smart trail selection, and progressive skill-building. If you want the full deep dive into advanced strategies, equipment upgrades, and long-term training, check out our Mountain Biking Guide.
Essential Mountain Biking Gear for New Riders
Starting mountain biking requires the right equipment to ensure safety and enjoyment on trails. Quality gear protects you while building confidence on technical terrain. Smart equipment choices prevent common beginner injuries and mechanical problems during rides.
| Gear Category | Essential Items | Beginner Recommendations |
| Mountain Bike | Hardtail MTB | Front suspension, easier maintenance |
| Safety Gear | Helmet, gloves, pads | Trail helmet with extra coverage |
| Hydration | Water bottle/pack | CamelBak style for longer rides |
| Repair Kit | Tools and spares | Tube, pump, tire levers, multitool |
Priority gear for beginner mountain biking:
- Properly fitted mountain bike helmet – protects head during falls
- Mountain biking gloves – improve grip and protect hands
- Knee and elbow pads – reduce injury risk on technical trails
- Hydration system – stay energized during longer MTB adventures
Additional essentials:
- Cycling glasses – protect eyes from branches and debris
- Sturdy closed-toe shoes – provide pedal grip and foot protection
- Basic repair kit – handle common trail mechanical issues
Starting with quality basics builds a foundation for years of mountain biking enjoyment.
Fundamental Mountain Biking Techniques
Proper riding technique transforms challenging trails into manageable adventures for beginner mountain biking enthusiasts. Body positioning and bike control skills prevent crashes while building confidence. Master these fundamentals before attempting advanced MTB features or technical terrain.
Body positioning essentials:
- Keep elbows out and knees bent for shock absorption
- Stay loose and relaxed over rough terrain and obstacles
- Maintain centered balance point between front and rear wheels
- Allow bike to move naturally underneath your body
Braking and gear management:
- Use both front and rear brakes evenly for controlled stopping
- Brake before corners and technical sections, not during turns
- Shift gears early before steep climbs or descents begin
- Avoid shifting under heavy pedal pressure to prevent chain issues
Climbing technique:
- Stay seated in saddle for better traction on climbs
- Lean forward slightly to keep front wheel planted
- Spin pedals smoothly rather than mashing big gears uphill
Descending fundamentals:
- Stand slightly off saddle with knees and elbows bent
- Keep weight back to prevent going over handlebars
- Let mountain bike move and absorb terrain underneath you
These core MTB skills create the foundation for safe and enjoyable trail riding.
Mountain Biking Trail Etiquette and Safety
Responsible trail behavior ensures mountain biking remains welcome in natural areas nationwide. Following established etiquette rules prevents conflicts between different trail user groups. Good trail citizenship protects riding access for future MTB generations.
Essential yield rules:
- Mountain bikers yield right-of-way to hikers and equestrians
- Downhill riders yield to uphill climbers on narrow trails
- Faster riders announce themselves before passing slower trail users
- Stop completely when encountering horses to avoid spooking animals
Environmental responsibility:
- Stay on designated trails – avoid creating new paths
- Never cut switchbacks or ride around muddy trail sections
- Pack out all trash and food waste completely
- Avoid riding on wet trails that damage easily
Communication and safety:
- Use bell or friendly voice when approaching other users
- Announce “rider up” or “passing on left” clearly
- Ride with buddies, especially on remote or technical trails
- Carry emergency contact information and basic first aid supplies
Trail maintenance support:
- Join local mountain biking advocacy groups and trail days
- Report trail damage or safety hazards to land managers
- Volunteer for trail building and maintenance projects regularly
Respectful mountain biking behavior maintains positive relationships with land managers and communities.
Getting Started on Mountain Bike Trails
Beginning mountain biking requires gradual progression through increasingly challenging trail systems. Start with easy green trails before attempting intermediate blue routes. Building skills systematically prevents injuries while developing confidence on technical MTB terrain.
| Trail Difficulty | Features | Best For |
| Green (Beginner) | Smooth, wide, gentle grades | First-time MTB riders |
| Blue (Intermediate) | Some rocks, roots, steeper sections | Developing skills |
| Black (Advanced) | Technical features, drops, jumps | Experienced riders |
Smart progression strategy:
- Master green trails completely before attempting blue difficulty routes
- Ride familiar trails multiple times to build muscle memory
- Practice skills on easy terrain before applying to challenges
- Join local mountain biking groups for mentorship and safety
Safety considerations for new riders:
- Always inform someone about your planned riding route and timing
- Carry fully charged phone for emergency communication needs
- Start with shorter rides to build endurance gradually
- Choose popular trails with regular foot traffic initially
Finding beginner-friendly trails:
- Use Google Maps to locate nearby trail systems and parks
- Check local bike shop recommendations for beginner routes
- Research trail conditions and difficulty ratings before visiting
Group riding benefits:
- Learn from experienced mountain biking riders and their techniques
- Increased safety through buddy system on remote trails
- Motivation to try new challenges with supportive encouragement
Smart trail selection accelerates learning while maintaining safety during your mountain biking journey.
Building Your Mountain Biking Skills Progressively
Developing advanced MTB abilities requires focused practice on specific techniques and features. Skill progression should follow logical steps from basic to complex maneuvers. Dedicated practice sessions improve confidence and safety on challenging mountain biking terrain.
Fundamental skill development areas:
- Cornering technique – practice smooth turns in open areas first
- Track standing – learn to balance while stopped for tight spaces
- Small obstacles – master rollovers before attempting larger trail features
- Speed control – develop confidence with braking and body positioning
Practice progression methods:
- Find empty parking lots or fields for initial skill practice
- Progress from flat ground to gentle slopes gradually
- Master each skill completely before combining with others
- Practice regularly rather than only during trail rides
Advanced technique building:
- Small drops and jumps – start with 6-inch features maximum
- Rock gardens – learn to pick lines through technical sections
- Steep descents – gradually increase comfort with challenging terrain
- Tight switchbacks – develop precision turning and balance skills
Learning resources:
- Consider professional mountain biking skills clinics in your area
- Watch instructional videos from reputable MTB coaching sources
- Practice with experienced riders who can provide feedback
- Focus on one skill per practice session for better retention
Progress tracking:
- Set achievable goals for each riding season
- Document successful completion of new trail features
- Celebrate skill improvements rather than comparing to others
- Take breaks when frustrated to prevent developing bad habits
Consistent skill practice transforms beginner mountain biking into confident trail mastery over time.